We read stories and fairy tales for children in syllables. Texts for reading We read fairy tales by syllables online with a child
A child who has learned to put sounds into syllables, syllables into words, and words into sentences needs to improve his reading skill through systematic training. But reading is a rather laborious and monotonous activity, and many children lose interest in it. Therefore we offer small texts words are divided into syllables.
First read the story to your child, and if it is long, you can read its beginning. This will interest the child. Then invite him to read the text. After each work, questions are given that help the child to understand what they have read and comprehend the basic information that they have learned from the text. After discussing the text, suggest reading it again.
Smart Bo-beak
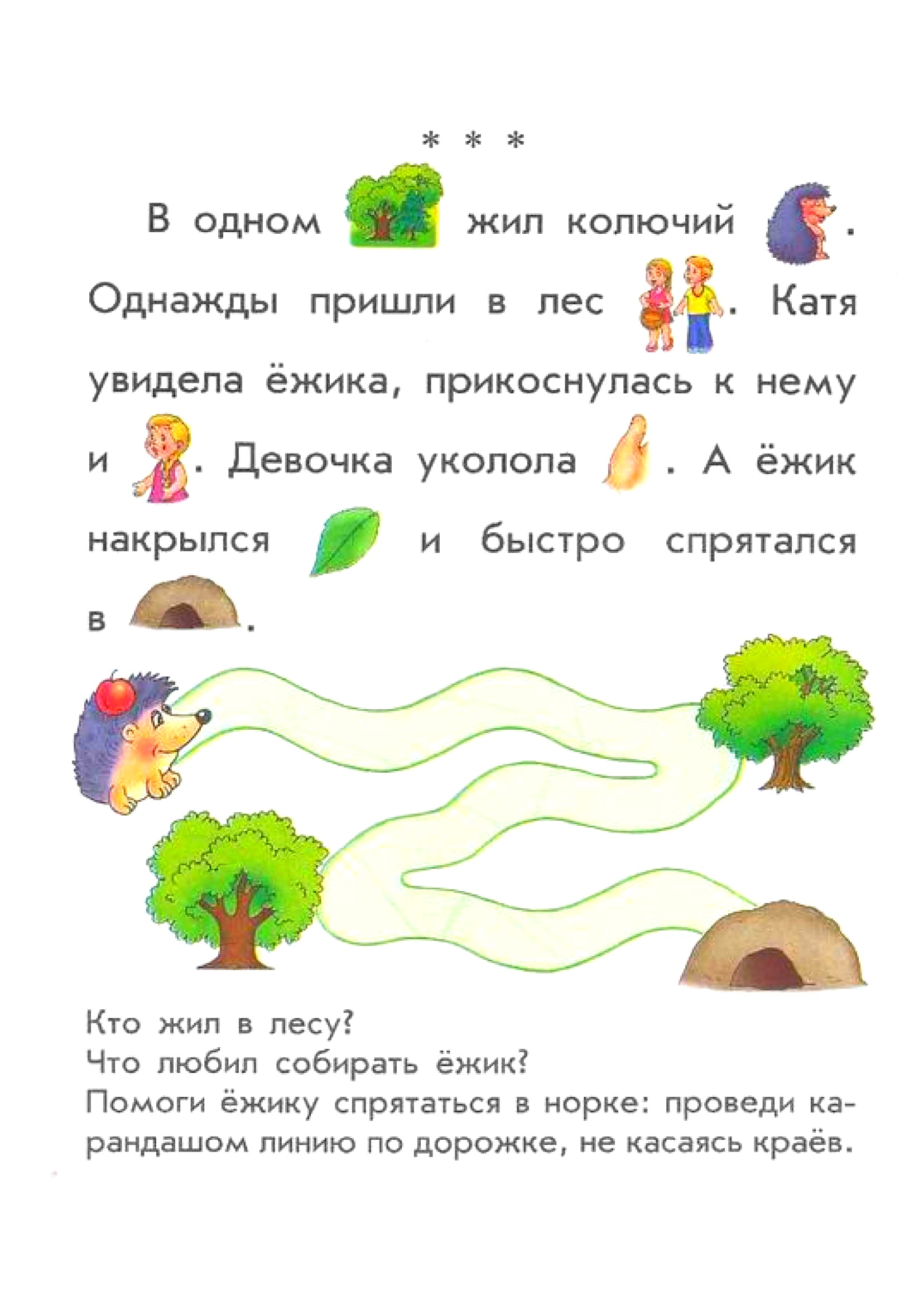
So-nya and co-ba-ka Bo-beak gu-la-li.
So-nya played-ra-la with a doll.
Therefore, So-nya be-be-zha-la to-my, and the doll for-would-la.
Bo-bik found a doll-lu and brought it to So-ne.
B. Korsunskaya
Answer the questions.
1. Who did Sonya walk with?
2. Where did Sonya leave her doll?
3. Who brought the doll home?
The bird made a nest on a bush. De-ti our nest-up and took off on the ground.
- Look, Vasya, three birds!
In the morning, de-ti came, and the nest-before it was empty. It would be a pity.
L. Tolstoy
Answer the questions.
1. What did the children do with the nest?
2. Why was the nest empty the next morning?
3. Did the children do well? How would you do?
4. Do you think this work is a fairy tale, a story or a poem?
Pet-ti and Mi-shi had a horse. They began to argue: whose horse. Did they tear each other apart.
- Give me - my horse.
- No, you give me - the horse is not yours, but mine.
Mother came, took a horse, and nobody's horse became.
L. Tolstoy
Answer the questions.
1. Why did Petya and Misha quarrel?
2. What did mom do?
3. Did the children play horse well? Why are you so
think?

It is advisable to use the example of these works to show children the genre features of poems, stories and fairy tales.
A genre of oral fiction containing events unusual in the everyday sense (fantastic, miraculous or worldly) and distinguished by a special compositional and stylistic construction. In fairy tales there are fairy-tale characters, talking animals, unprecedented miracles happen.
Poem- a small piece of poetry in verse. The verses are read smoothly and musically, they have rhythm, meter and rhyme.
Story- small literary form; a narrative work of small volume with a small number of characters and the short duration of the events depicted. The story describes a case from life, some bright event that really happened or could happen.
In order not to discourage reading, do not force him to read texts that are uninteresting and inaccessible to his understanding. It happens that a child takes a book he knows and reads it “by heart”. Necessarily read to your child every day poems, fairy tales, stories.
Daily reading enhances emotionality, develops culture, horizons and intellect, helps to understand human experience.
Literature:
Koldina D.N. I read on my own. - M.: TC Sphere, 2011. - 32 p. (Candy).
Children's texts for reading by syllables. Read on your own. When a child learns to read, some children need to read syllable by syllable, and some are more comfortable reading in full words without dashes. The page provides simple texts in both versions. We read in syllables.
There would be thunder. It was pouring heavy rain. Gre-chalk thunder. Stre-ko-za-bra-la-s under the mushroom. Mi-mo on do-ro-ge half-evil u-lit-ka. Stre-ko-for go-vo-rit:
- Wu-lit-ka, w-lit-ka! Come to me. Here soo-ho, like under. roofs.
- I don't need a roof! My house is with me.
Thunderstorm
There was a thunderstorm. It was pouring heavy rain. Thunder rumbled. The dragonfly climbed under the mushroom. A snail was crawling along the road. Dragonfly says:
- Snail, snail! Come to me. It's dry as hell in here. roof.
I don't need a roof! My house is with me.
It's not just a ve-dot
Mi-sha slo-small ma-le-n-cue du-bok.
- Why did you do this? - oh-gor-chi-la-s Ma-sha.
- Yes, it's just a hundred ve-dot-ka!
“No, you po-gu-beat pain-sho-e, mo-gu-che-de-re-vo,” said Ma-sha.
It's not just a branch
Misha broke a small oak tree.
– Why did you do it? Masha was upset.
- Yes, it's just a twig!
“No, you destroyed a big, mighty tree,” said Masha.
Ze-blah-no-ka
Re-bya-ta gu-la-li in the forest. Went-la Na-dya on-la-well. Looks: oh-ko-lo no-e red-we-e I-go-dy. I-a year would-lo not-much. Na-dya collected them in la-dosh-ku, but didn’t eat.
-Petya! Vasya! Come to me! Earth-la-no-ka! Per-va-I earth-la-no-ka!
When-be-zha-whether be-bya-ta. And everyone is two years old
- Oh, how taste-but!
Soon the earth-la-no-ki will be a lot. But the first I-go-dy-sa-we-e sun-nye.
strawberries
The children were walking in the forest. Nadia stepped out into the clearing. Looks: there are red berries near her. There were few berries. Nadia gathered them in her palm, but did not eat.
-Petya! Vasya! Come to me! Strawberries! First strawberry!
The guys came running. And everyone has two berries.
-Oh, how delicious!
There will be plenty of strawberries soon. But the first berries are the most delicious.
Morning
The boy and de-vo-chka go to school.
And Le-na drinks tea.
- Daughter, it's already seven o'clock! - go-vo-rit ma-ma
Le-na looks at the watch.
-Our watch is too-three, ma-moch-ka!
- No, Le-noch-ka. Hours are right. And you de-la-eat everything honey-le-no.
Morning
Boy and girl go to school.
And Lena drinks tea.
- Daughter, it's already eight o'clock! - Mom says
Lena looks at her watch.
-Our clock is going too fast, mommy!
- No, Lenochka. The clock is running right. And you do everything slowly.
Your baby has learned letters, actively adds syllables and small words. It's time to move on to more complex, but interesting tasks - reading texts. But here parents and teachers expect some difficulties. It is impossible to offer a preschooler text cards without taking into account the characteristics of age, the degree of development of the skill of syllable reading. We will tell you in our article how to choose texts for reading for preschoolers, where to find and how to correctly print texts for reading by syllables for younger and older preschoolers.
Age features of preschoolers
Kindergarteners after 5 years are very active, mobile, inquisitive. They rapidly grow up, grow wiser, develop physically and mentally.
When preparing for school, parents, teachers should pay attention to the following age characteristics of kids 4-7 years old:
- The main need of kindergarteners is communication, games. Children ask a lot of questions to adults, themselves, peers. Learn by playing.
- The leading mental function is imagination, fantasy. This helps to show creativity.
- Emotions, impressions, positive experiences are important for further development, desire to continue activities. Kindergartener 5-7 years old needs praise, support, lack of comparison with other children.
- Cognitive processes are actively developing: attention, memory. At 5-7 years old, preschoolers can remember and analyze a large amount of information. But you need to give it in doses, trying not to overload the children's brain in one lesson.
- Speech becomes more developed. At the age of 5, the kid speaks in complex sentences, can pick up several synonyms for one word, knows a lot of poems, riddles, and several fairy tales by heart.
- Kindergartener wants to learn new things and learn. The kid is spurred on by curiosity, he is interested in everything new, unknown.
Consider age and individual characteristics preschoolers choosing texts to read. In this case, the training sessions will be more effective.
How to work with texts
Reading poems, short stories for a preschooler is a new kind of work. The difficulty of completing the reading task lies in the fact that the kindergartener does not always understand the meaning of the passage. To avoid this, you need to approach the choice of material and methods of its processing correctly. Build the learning process as follows:
- Select handouts according to the age of the student. For kids 4-5 years old, cards of 1-3 sentences, for older preschoolers - 4-5 sentences.
- Pay attention to the number of words in the sentences. There should be few of them. Simple texts for reading for preschoolers are easier to digest, but you can’t stay at an easy level for a long time.
- Move on to working with text cards after automating syllabic reading.
- Read in a chain in a group or together with adults in individual work.
- Don't rush your child. At the learning stage, reading comprehension is important, not the speed of reading and the amount of time spent.








Texts for children 4-5 years old
Young preschoolers need special suggestion cards. Reading by syllables for children under 5 years old is best accompanied by text with pictures. For example, coloring pages with comments. Coloring will be an additional task.
If for the first time we read by syllables, the texts for reading should consist of 1-2 sentences. Use small words, 1-2 syllables. Cards can be prepared independently, found on the web and printed.
For young students, it is important that there is a hyphen or other separator between syllables. Choose a font for printing material for reading by syllables at 4 years old, large, bold.
- Learning to read by syllables through working with text does not have to begin after learning the entire alphabet. Find for reading to children from 5 years old and print out individual sentences from such words, which consist of learned letters. There are many of them in the Zhukova alphabet.
- At the age of 4 to 5 years, it is not necessary to offer children a whole fairy tale, a book. Large volumes scare kids, distract with colorful drawings on other pages. Print only the section you want.
- Play with a passage, a poem. You can read a word separately, then a phrase, then a whole syntactic unit.
- Work according to the following algorithm. First we read, then we discuss, draw, fantasize.





Tasks
After reading the texts, be sure to study the material additionally. This is necessary for a solid assimilation of information, the formation of meaningful reading skills. Suggest to preschoolers the following types tasks for the passage:
- Short retelling.
The kindergartener should tell what he learned, what information was the main thing in the text. It is advisable to use the words read, to name the names of the characters, their actions. - Answer the questions.
Speech therapist, parent ask 1-3 simple questions about the material read.
If the baby does not answer them, you need to read the passage together, with the adult's comments. - Draw a picture.
We play illustrators. Children come up with a plot picture based on the information received from the passage, the poem. It could be homework. - What happened next?
Offer to dream up, think of what could happen to the characters next.
Reading texts with pictures and tasks:















Texts for children 6-7 years old
If you are preparing reading texts for children 6-7 years old, then you can print out entire paragraphs. For work, choose excerpts from fairy tales, short stories. With large works, you can work 2-3 lessons. Do not forget about short stories from the alphabet or primer.
- Work through the sentences in a chain, try to involve each student.
- After reading the short passage for the first time, discuss the content. If you find any misunderstandings of the information, read the passage again.
- If we read individually by syllables, different texts for reading to children of 7 years old should be printed on separate sheets.
Texts with tails:










Russian folk tale"Baba Yaga" in pictures. The text is divided into syllables to make it easier to read.
Print the pages, fasten with a stapler, you get a coloring book. You can read the story and color the pictures.
Below is just the text of the tale in syllables.
In the archive you will find both text and pictures.
















Download file: (downloads: 285)
Zhi-la - would-la de-voch-ka. Called e-yo A-le-nush-koy. Native ma-tush-ki didn’t have-lo. And o-tets same-nil-sya on an evil ma-che-he.
Don’t-want-bi-la ma-che-ha A-le-nush-ku and for-ho-te-la e-e with the light to live. Called o-on pad-che-ri-tsu and go-vo-rit: - Go-pay to my sister-tre, from-not-si to her ba-ra-no-check.
A-le-nush-ka went through the ancient forest to look for ma-che-hee-well sister-true. I-child, but my self is so scary!
U-wee-de-la o-na from bush-ku on chicken-knives. Si-dit on le-sen-ke black cat and shi-pit on de-voch-ku. But A-le-nush-ka in-gla-di-la e-go on the sher-stke and y-gos-ti-la ba-ra-night-coy.
The cat to her and go-vo-rit: - Spa-si-bo, good-ra-I de-voch-ka. Run fast from here, yes, here Ba-ba Ya-ha lives. Soon must come.
Here, indeed, everything is for-gro-ho-ta-lo: let-tit Ba-ba Ya-ga Kos-tya-na-ya No-ga in de-re-vyan-noy stu-pe, in me -scrap times-ma-hi-va-et.
- Go-in-ri, why did you come, or else I’ll eat you!
Ras-ska-za-la to her A-le-nush-ka about ma-che-hu.
- Ho-ro-sho, - go-vo-rit Ba-ba Ya-ga.
- Po-ka-zhu-be-do-ro-gu to ma-che-hee-noy ses-tre, if you are so-kyo-kyo by-lot-but yes de-syat ru-ba- shek me sew-eat.
And if you don’t eat, I’ll eat you.
Za-pla-ka-la A-le-nush-ka, and the cat says to her:
- Do not worry. Run to my.
I will do all the work for you. And you take a comb and in-lo-ten-tse be-lo-e - oh-no you-be-go-dyat-sya.
Po-bla-go-da-ri-la
Sat down ko-tik on-lot-but weave. Ba-ba Ya-ga cry-chit from the yard:
- Do you weave in a lot-but, de-vi-tsa?
- Weaving, weaving, - from-ve-cha-et ko-tic.
Ba-ba I-ga for-look-well-la in the ok-but and nya-la, what is it about-ma-well-whether. Ki-nu-las o-na in ho-nu.
Og-la-well-las A-le-nush-ka: Ba-ba Ya-ga e-e to-go-nya-et.
Bro-si-la o-on-then-yes-lo-ten-tse be-lo-e behind the back-well - there was a re-ka shi-ro-ka-ya.
Ba-ba Ya-ga bul-tyh in the water. On-si-lu got out and again in go-nu bro-si-las. Sov-this is already up to-go-nya-et A-le-nush-ku.
Bro-si-la then-yes A-le-nush-ka gre-ben - you-grew-behind-di forest thick and dre-mu-chi. And sa-ma further on-be-zha-la.
Sta-la Ba-ba Ya-ga through the forest pro-bi-army-sya: de-re-vya stand you-so-ki-e, ko-rya-gi lie ko-rya-you-e , kick tor-chat thick-e.
Og-la-well-losed A-le-nush-ka and sees: at the same time Ba-ba Ya-ga Kos-tya-on-I No-ha - you are completely out of your strength b-lass!
Pri-be-zha-la A-le-nush-ka do-my and ras-ska-for-la ba-tyush-ke, how ho-te-la ruin e-yo ma-che-ha and how the black cat e-yo from Ba-would I-gi saved.
Ras-ser-dil-sya about-father on ma-che-hu and kicked e-e out of the house.
- Don't you hurt me - get away!
And the black cat-tick in the state came to A-le-nush-ke.
In-gos-til - in-guest-silt ko-tik and for-ever-yes live os-tal-sya. That would be joy-la A-le-nush-ke!
Dear readers!
All materials from the site can be downloaded absolutely free of charge. All files are checked by antivirus and do not contain hidden scripts.
Pictures in the archives are not watermarked.
The site is replenished with materials based on the free work of the authors. If you want to thank them for their work and support our project, you can transfer any amount that is not burdensome for you to the site's account.
Thank you in advance!!!
Learning to read in syllables - this stage in teaching children to read is one of the most important and difficult. Often parents simply do not know how to teach a child to pronounce two letters together and get stuck on it for a long time. Tired of the endless repetition of "ME and A will be MA", the child quickly loses interest, and learning to read turns into torment for the whole family. As a result, children who already know letters from the age of two or three cannot even read simple words by the age of five, not to mention reading sentences and books.
What to do next when the child has memorized the letters? Let's make a reservation right away that teaching a preschooler to read syllables can be started even BEFORE he has mastered the entire alphabet (moreover, some teachers insist that you need to move on to syllables as quickly as possible, without waiting for all the letters to be studied). But those letters that we will combine into syllables, the child must name without hesitation.
In order to start learning to read by syllables, it is enough for a child to know 3-4 vowels and a few consonants. First of all, take those consonants that can be pulled (S, Z, L, M, N, V, F), this will help teach the child the continuous pronunciation of the syllable. And this is a fundamentally important point.
So, let's consider a few, in our opinion, the most effective methods that modern teachers offer for teaching a child to fold letters into syllables.
1. We play "Engines"
(a game from the manual by E. Baranova, O. Razumovskaya "How to teach your child to read").
Instead of boring cramming, invite your child to "ride the train." All consonants are written on the rails along which our trailers will go, and vowels are written on the trailers themselves. We place the trailer on the rails so that a consonant appears in the window, and we name which station we got (for example, BA). Next, we move the trailer down the rails - to the next consonant and read the syllable that appears.
There is a similar guide in cards "Game" Steam locomotive. We read syllables. from E. Sataeva
This game is good because the child does not need to be specially explained how to add syllables. It is enough to say: “Now we will ride the letter A, she will be our passenger, name all the stations at which we will make a stop.” To begin with, “ride” yourself - let the child move the trailer along the rails, and you loudly and clearly call the “stations”: BA, VA, GA, YES, ZHA, ZA, etc. Then invite your child to take turns doing this with you. During the game, listening to you, children easily grasp how to pronounce two sounds together. For the third time, the child will “ride” himself without much difficulty.
If the child does not know all the letters, stop only at those “stations” that are familiar to him. Next, we change the wagon. Now we roll the letters O, U, S. If the child can easily cope with the task, we complicate the task. For example, we ride at speed - timing which of the wagons will reach the end of the path first. Or another option: stopping at the station, the child should name not only the syllable, but also the words starting with this syllable (BO - barrel, side, Borya; VO - wolf, air, eight; GO - city, golfs, guests; DO - rain, daughter, boards, etc.).
Please note that with this game you can practice reading not only open syllables (with a vowel at the end), but also closed ones (with a consonant at the end).
To do this, we take trailers where the vowels are written in front of the window, and act in the same way. Now we have a letter on the trailer not a passenger, but a driver, she is the main one, she is in front. First read the resulting “stations” with closed syllables yourself: AB, AB, AG, AD, AZH, AZ, etc., then offer the child a “ride”.
Remember that in this and other exercises, we first practice adding syllables with first-row vowels (A, O, E, Y, Y), and then we introduce second-row vowels (I, E, E, Yu, I) - the so-called "iotized" vowels, which make the sound that precedes them soft.
When the child is good at reading separate tracks with syllables, alternate wagons with passengers and drivers, without prompting which wagon we will roll. This will help the child learn to clearly see exactly where the vowel is in the syllable (the syllable begins with it or ends with it). At first, learning to read by syllables in a child may have difficulties with this.
2. "Run" from one letter to another
(from "ABC for kids" by O. Zhukova)This is a visual exercise that will help the child learn to pronounce two letters together.

Before us is a path from one letter to another. To overcome it, you need to pull the first letter until the finger that we are leading along the path reaches the second letter. The main thing we are working on in this exercise is that there is no pause between the first and second sound. In order to make it more interesting to study, replace your finger with a figure of any animal / little man - let him run along the path and connect two letters.
("ABC book for kids" by E. Bakhtina, "Russian alphabet" by O. Zhukova and others).
 Many authors of primers and alphabets use animated images of letters that need to be folded into a syllable - they are friends, walk together in pairs, pull each other through obstacles. The main thing in such tasks, as in the previous exercise, is to name two letters together so that the two girlfriend letters stay together.
Many authors of primers and alphabets use animated images of letters that need to be folded into a syllable - they are friends, walk together in pairs, pull each other through obstacles. The main thing in such tasks, as in the previous exercise, is to name two letters together so that the two girlfriend letters stay together.

To use this technique, you do not even need special manuals or primers. Print out several figures of boys and girls (animals, fairy-tale or fictional characters), write a letter on each of them. Let consonants be written on the figures of boys, and vowels on the figures of girls. Make friends with the kids. Check with your child that boys and girls or two girls can be friends, but it is not possible to make friends with two boys (pronounce two consonants together). Change pairs, put girls first in them, and then boys.

Read the syllables first in one order, then in reverse.
These few tricks are quite enough to teach a child to put two letters into a syllable. And learning in the form of a game will allow you to avoid cramming and boring repetition of the same thing.
4. Games to consolidate the skill of adding letters
- Syllabic Lotto
It is very easy to make them yourself, for this you need to pick up a few pictures - 6 for each card and print the corresponding syllables.

- Help will help you “Syllables. Choose a picture according to the first syllable BA-, VA-, MA-, SA-, TA-. Educational lotto games. GEF DO "E. V. Vasilyeva- there are a few more tutorials in this series “Letters, syllables and words. Lotto with verification” by A. Anikushena
- Similar exercises are in the book. "Syllabic tables. GEF "N. Neshchaeva
- Shop game
Lay out toy goods or pictures with their images on the counter (for example, FISH-ba, DY-nya, PI-horns, BU-lka, YaB-loki, MYA-so). Prepare "money" - pieces of paper with the name of the first syllables of these words. A child can buy goods only for those “bills” on which the correct syllable is written.
Make an album with your child’s own hands, in which a syllable will be written on one page of the spread, and objects whose name begins with this syllable will be written on the other. Periodically review and supplement these albums. For more effective learning to read, close one or the other half of the turn (so that the child does not have extra clues when naming a syllable or choosing words for a particular syllable).

This will help you "Cards for sound and syllabic analysis of words."
- Game in the airfield (garages)
We write syllables large on sheets of paper, lay them out around the room. These will be different airfields (garages) in our game. The child takes a toy plane (car), and the adult commands - on which airfield (in which garage) you need to land the plane (park the car).
For this exercise, Zaitsev cubes or any cards with syllables are suitable (you can make them in the form of traces). We build a long path from them - from one end of the room to the other. Choose two figurines / toys. You play one, the child plays the other. Roll the dice - take turns with your figures on the cards for as many moves as fell on the dice. Stepping on each card, name the syllable written on it.
For this game, you can also use various "walkers" by writing syllables in circles on the playing field.

5. Reading simple words by syllables
Simultaneously with the development of syllables, we begin to read simple words(of three or four letters). For clarity, so that the child understands what parts the word consists of, which letters should be read together and which separately, we recommend that the first words be composed of cards with syllables / individual letters or graphically divide the word into parts.

Words of two syllables can be written on pictures consisting of two parts. Pictures are easier to understand (the child is more willing to read the words written on them than just columns of words), plus it is clearly visible into which parts a word can be broken down when reading it syllable by syllable.

Increase the difficulty gradually: start with words consisting of one syllable (UM, OH, EM, UZH, Hedgehog) or two identical syllables: MOM, UNCLE, DAD, NANNYA. Then proceed to reading the words of three letters (closed syllable + consonant): BAL, SON, LAK, BOK, HOUSE.
You need to understand that even if a child pronounces all the syllables in a word correctly, this does not mean that he will immediately be able to meaningfully put them into a word. Be patient. If a child has difficulty reading words of 3-4 letters, do not proceed to reading longer words and especially sentences.
Be prepared for the fact that the child will freely begin to read words only after he has automated the skill of adding letters into syllables. Until this happens, periodically return to working out syllables.
And, most importantly, remember that any learning should be a joy - for both parents and children!
Philologist, teacher of Russian language and literature, teacher preschool education
Svetlana Zyryanova
